
Ensuring Safety at Sea
The International Maritime Organization (IMO) has approved amendments to SOLAS Regulation V/23, establishing stricter and clearer requirements for pilot transfer arrangements. These changes will enhance the safety of maritime pilots and crew during embarkation and disembarkation operations.
Why This Update?
Pilot transfer remains a critical and high-risk operation. Over the years, accidents involving improperly rigged or non-compliant pilot ladders have resulted in injuries and fatalities. The new SOLAS amendments, developed in collaboration with the International Maritime Pilots’ Association (IMPA), ensure that safety requirements are mandatory and not subject to interpretation.
Timeline of Implementation
• December 2024: Approval of the amendments by the IMO Maritime Safety Committee.
• June 2025: Final adoption at MSC 110.
• January 1, 2028: New regulations enter into force globally.
• 2029-2030: Existing ships must comply with the new rules during scheduled surveys.
Binding International Law
The SOLAS Convention (Safety of Life at Sea) is a legally binding treaty for IMO member states. This means that once the amendments are adopted, they must be incorporated into the national laws of all member states, ensuring global compliance.
Structure of the New Regulations
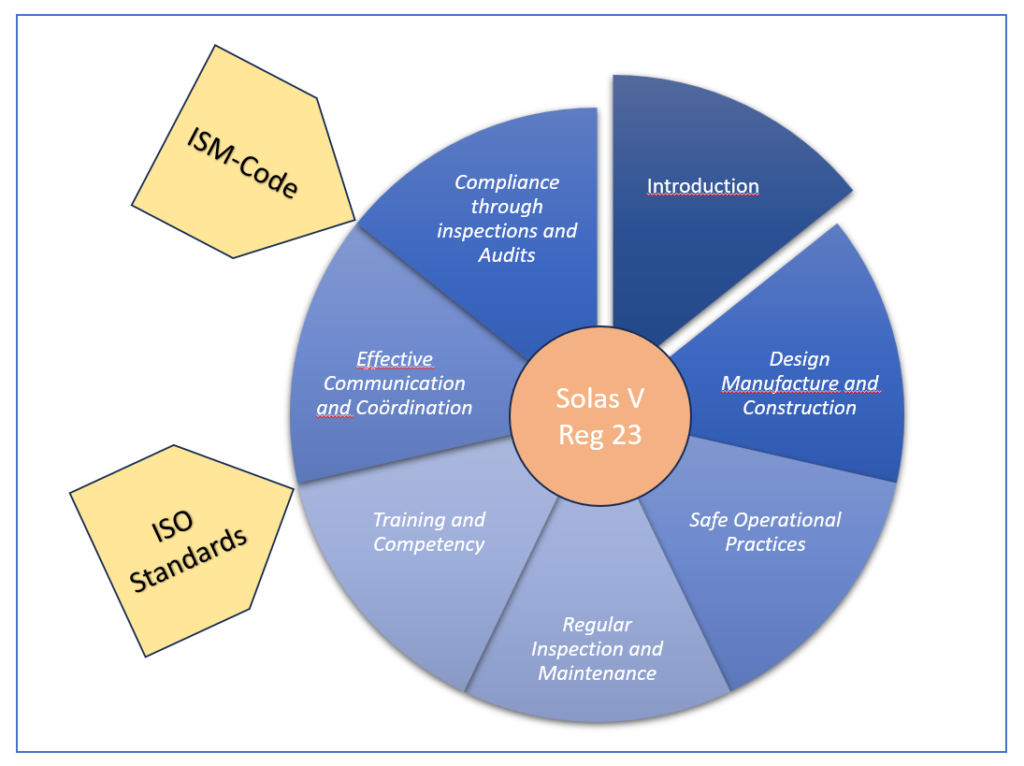
Structure of the New Regulations
Solas Regulation V/23 text
The revised SOLAS V/23 mandates safer pilot transfer arrangements from January 1, 2028. New installations must comply with strict IMO standards, while existing systems must be compliant by 2030. Mechanical hoists are banned, lighting is required, and inspection and maintenance rules are strengthened. Crew training is mandatory. Early implementation is encouraged. The amendments become legally binding after formal IMO approval in June 2025, with enforcement through flag states and Port State Control. This enhances pilot transfer safety and requires shipowners to take timely action to ensure compliance.
Introduction
Establishes mandatory requirements for the safe design, construction, rigging, installation, and maintenance of pilot transfer arrangements (PTAs).
This section defines the overall safety objectives and clarifies the obligations of ship operators to provide safe and compliant pilot transfer arrangements.
Part A – Design, Manufacture, and Construction
Establishes the standards for the materials and construction of pilot ladders, accommodation ladders, and securing arrangements.
Minimum material strength, step spacing, ladder securing methods, prohibition of unsafe securing methods (e.g., shackles or knots).
Part B – Rigging
Specifies how pilot ladders and accommodation ladders must be rigged to ensure safe use.
Secure attachment points, clearances, use of retrieval lines, and height requirements based on sea conditions.
Part C – Installation of Pilot Ladder Winch Reels
Establishes installation and operational requirements for pilot ladder winch reels.
Safe operation, mechanical securing, proper positioning, and requirements for manual and powered winch reels.
Part D – Operational Readiness, Onboard Inspection, and Maintenance
Defines shipowner responsibilities for ensuring PTAs remain in good working order.
Pre-use and post-use inspections, periodic maintenance, mandatory replacement intervals for pilot ladders.
Part E – Familiarization
Ensures that ship crews are trained to correctly rig, inspect, and maintain PTAs.
Crew training on ladder use, identification of non-compliant setups, and responsibilities of officers in charge.
Part F – Approval
Establishes approval procedures for PTAs by maritime administrations.
Type-approval process, manufacturer certification, and regulatory compliance checks during ship inspections.
The Role of the ISM Code and ISO 799 in PTA Safety
ISM Code
The International Safety Management (ISM) Code requires ships to have documented procedures for pilot transfer safety.
Ensures that companies implement safe operational practices, provide crew training, and maintain compliance with SOLAS regulations.
ISO 799
Provides technical specifications for the design and construction of pilot ladders.
Ensures that all ladders meet minimum safety standards for material strength, step dimensions, and securing methods.
🧠 Test Your Knowledge!
- What is the primary purpose of the new SOLAS amendments to pilot transfer arrangements?
- A) To reduce the cost of pilot ladders
- B) To standardize pilot ladder designs for aesthetic reasons
- C) To improve safety and ensure compliance with stricter regulations
✅ Correct Answer: C) The amendments are designed to enhance safety and enforce stricter compliance measures for pilot transfer arrangements.
- Which section of the new regulations focuses on crew training and competency?
- A) Part A – Design and Construction
- B) Part E – Familiarization
- C) Part C – Installation of Pilot Ladder Winch Reels
✅ Correct Answer: B) Part E ensures that crews receive proper training on the safe rigging and inspection of pilot ladders.
- How does ISO 799 contribute to pilot ladder safety?
- A) It establishes technical standards for ladder design and materials
- B) It provides general maritime safety recommendations
- C) It regulates the use of lifeboats
✅ Correct Answer: A) ISO 799 specifies construction and material standards for pilot ladders, ensuring they meet global safety requirements.
